Quick Start
Welcome to MemOS Cloud Platform. Refer to this guide to quickly integrate memory capabilities.
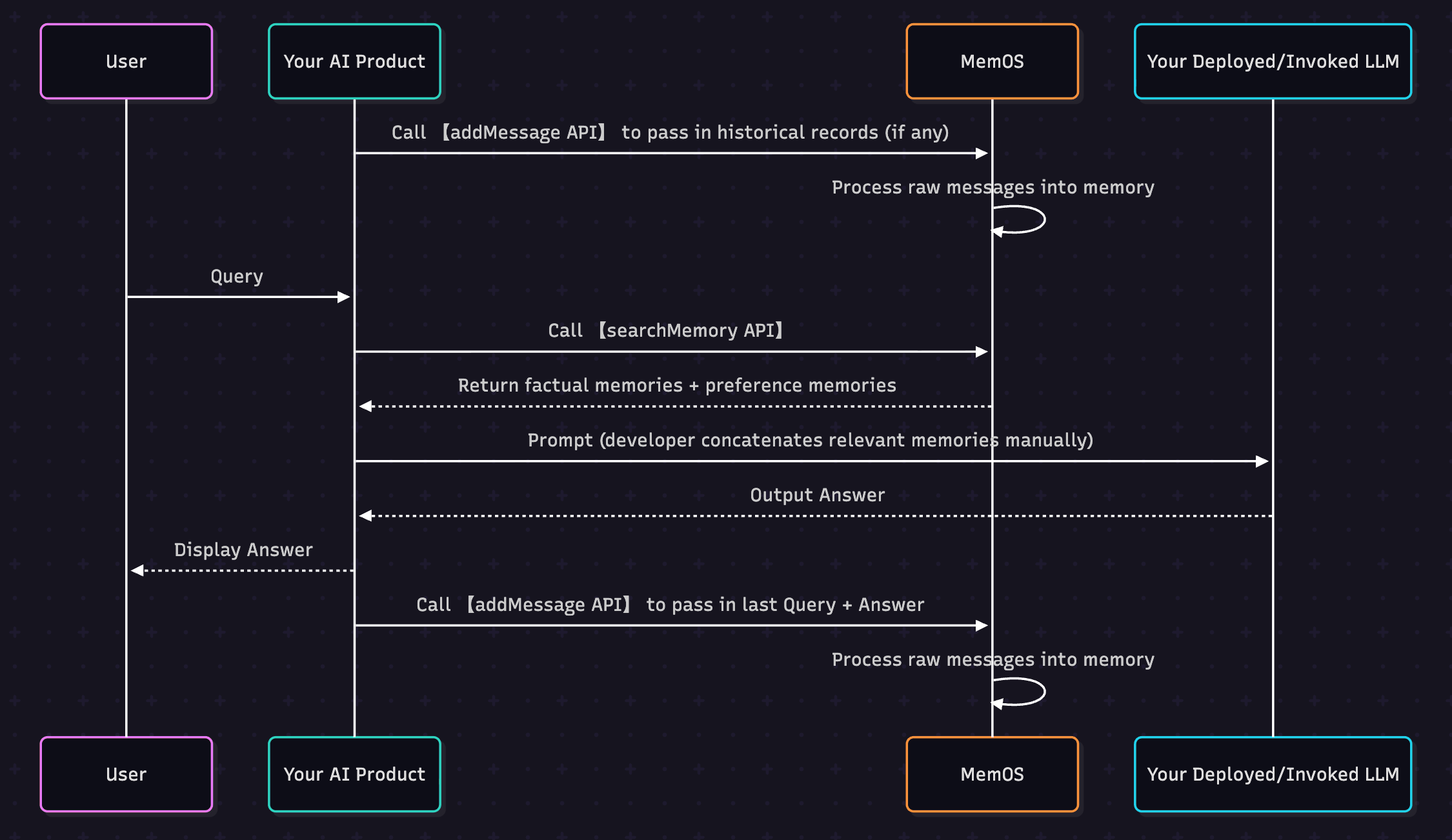
When building applications with large models, a common question is: How to make AI remember user's long-term preferences? MemOS provides two core interfaces to help you achieve this:
addMessage—— Hand over the original conversation to us, and we will automatically process and store memories (Click for detailed API documentation)searchMemory—— Recall memories in subsequent conversations to make AI answers more relevant to user needs (Click for detailed API documentation)
1. Preparation
- Register and log in to MemOS Cloud Platform (Click to Register);
- Get API Key (Click to Get);
- Prepare an environment capable of sending HTTP requests, such as Python or cURL.
2. Code Configuration
2.1 Install SDK
If you choose Python SDK, please ensure Python 3.10+ is installed, then execute:
pip install MemoryOS -U
2.2 Add Original Conversation (addMessage)
Session A: Occurred on 2025-06-10
You only need to provide the
You only need to provide the
original conversation records to MemOS, and MemOS will automatically abstract, process, and save them as memories.import os
import requests
import json
# Replace with your API Key
os.environ["MEMOS_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_API_KEY"
os.environ["MEMOS_BASE_URL"] = "https://memos.memtensor.cn/api/openmem/v1"
data = {
"user_id": "memos_user_123",
"conversation_id": "0610",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "I’ve planned to travel to Guangzhou this summer. What chain hotels are available for accommodation?"},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "You can consider options like 7 Days Inn, All Seasons, Hilton, etc."},
{"role": "user", "content": "I’ll choose 7 Days Inn."},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "Alright, feel free to ask me if you have any other questions."}
]
}
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": f"Token {os.environ['MEMOS_API_KEY']}"
}
url = f"{os.environ['MEMOS_BASE_URL']}/add/message"
res = requests.post(url=url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(data))
print(f"result: {res.json()}")
# Please ensure that MemOS has been installed (pip install MemoryOS -U)
from memos.api.client import MemOSClient
# Initialize MemOS client with API Key to start sending requests
client = MemOSClient(api_key="YOUR_API_KEY")
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": "I’ve planned to travel to Guangzhou this summer. What chain hotels are available for accommodation?"},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "You can consider options like 7 Days Inn, All Seasons, Hilton, etc."},
{"role": "user", "content": "I’ll choose 7 Days Inn."},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "Alright, feel free to ask me if you have any other questions."}
]
user_id = "memos_user_123"
conversation_id = "0610"
res = client.add_message(messages=messages, user_id=user_id, conversation_id=conversation_id)
print(f"result: {res}")
curl --request POST \
--url https://memos.memtensor.cn/api/openmem/v1/add/message \
--header 'Authorization: Token YOUR_API_KEY' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"user_id": "memos_user_123",
"conversation_id": "0610",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "I’ve planned to travel to Guangzhou this summer. What chain hotels are available for accommodation?"},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "You can consider options like 7 Days Inn, All Seasons, Hilton, etc."},
{"role": "user", "content": "I’ll choose 7 Days Inn."},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "Alright, feel free to ask me if you have any other questions."}
]
}'
2.3 Call MemOS to Search Relevant Memories in Session (searchMemory)
Session B: Occurred on 2025-09-28
In a new session, the user asks the AI to recommend travel destinations and hotels for the National Day holiday. MemOS automatically recalls Factual Memory: Where they have been and Preference Memory: Hotel booking preferences for AI reference, thereby recommending a more personalized travel plan.
In a new session, the user asks the AI to recommend travel destinations and hotels for the National Day holiday. MemOS automatically recalls Factual Memory: Where they have been and Preference Memory: Hotel booking preferences for AI reference, thereby recommending a more personalized travel plan.
import os
import requests
import json
# Replace with your API Key
os.environ["MEMOS_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_API_KEY"
os.environ["MEMOS_BASE_URL"] = "https://memos.memtensor.cn/api/openmem/v1"
data = {
"query": "I want to travel during the National Day holiday. Please recommend a city I haven’t been to and a hotel brand I haven’t stayed at.",
"user_id": "memos_user_123",
"conversation_id": "0928"
}
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": f"Token {os.environ['MEMOS_API_KEY']}"
}
url = f"{os.environ['MEMOS_BASE_URL']}/search/memory"
res = requests.post(url=url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(data))
print(f"result: {res.json()}")
# Please ensure that MemOS has been installed (pip install MemoryOS -U)
from memos.api.client import MemOSClient
# Initialize MemOS client with API Key to start sending requests
client = MemOSClient(api_key="YOUR_API_KEY")
query = "I want to travel during the National Day holiday. Please recommend a city I haven’t been to and a hotel brand I haven’t stayed at."
user_id = "memos_user_123"
conversation_id ="0928"
res = client.search_memory(query=query, user_id=user_id, conversation_id=conversation_id)
print(f"result: {res}")
curl --request POST \
--url https://memos.memtensor.cn/api/openmem/v1/search/memory \
--header 'Authorization: Token YOUR_API_KEY' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"query": "I want to travel during the National Day holiday. Please recommend a city I haven’t been to and a hotel brand I haven’t stayed at.",
"user_id": "memos_user_123",
"conversation_id": "0928"
}'
The output memory list is as follows:
# Example Output (Simplified for understanding, for reference only)
# Preference Type Memories
{
preference_detail_list [
{
"preference_type": "implicit_preference", # Implicit Preference
"preference": "User may prefer hotels with higher cost-performance ratio.",
"reasoning": "7 Days Inn is usually known for being economical. The user's choice of 7 Days Inn may indicate a preference for cost-effective options in accommodation. Although the user did not explicitly mention budget constraints or specific hotel preferences, choosing 7 Days among the provided options may reflect an emphasis on price and practicality.",
"conversation_id": "0610"
}
],
# Factual Type Memories
memory_detail_list [
{
"memory_key": "Summer Guangzhou Travel Plan",
"memory_value": "User plans to travel to Guangzhou during the summer vacation and chose 7 Days Inn as accommodation.",
"conversation_id": "0610",
"tags": [
"Travel",
"Guangzhou",
"Accommodation",
"Hotel"
]
}
]
}
2.4 Example of Assembling Memories into a Prompt
Memory Assembly
Using recalled memories requires certain techniques. Below is an assembly example.
Using recalled memories requires certain techniques. Below is an assembly example.
# Role
You are an intelligent assistant powered by MemOS. Your goal is to provide personalized and accurate responses by leveraging retrieved memory fragments, while strictly avoiding hallucinations caused by past AI inferences.
# System Context
- Current time: 2026-01-06 15:05 (Baseline for freshness)
# Memory Data
Below is the information retrieved by MemOS, categorized into "Facts" and "Preferences".
- **Facts**: May contain user attributes, historical logs, or third-party details.
- **Warning**: Content tagged with '[assistant观点]' or '[summary]' represents **past AI inferences**, NOT direct user quotes.
- **Preferences**: Explicit or implicit user requirements regarding response style and format.
<memories>
<facts>
-[2025-12-26 21:45] User plans to travel to Guangzhou during the summer vacation and chose 7 Days Inn as accommodation.
-[2025-12-26 14:26] The user's name is Grace.
</facts>
<preferences>
-[2026-01-04 20:41] [Explicit Preference] The user likes traveling to southern regions.
-[2025-12-26 21:45] [Implicit Preference] User may prefer hotels with higher cost-performance ratio.
</preferences>
</memories>
# Critical Protocol: Memory Safety
You must strictly execute the following **"Four-Step Verdict"**. If a memory fails any step, **DISCARD IT**:
1. **Source Verification (CRITICAL)**:
- **Core**: Distinguish between "User's Input" and "AI's Inference".
- If a memory is tagged as '[assistant观点]', treat it as a **hypothesis**, not a hard fact.
- *Example*: Memory says '[assistant view] User loves mango'. Do not treat this as absolute truth unless reaffirmed.
- **Principle: AI summaries have much lower authority than direct user statements.**
2. **Attribution Check**:
- Is the "Subject" of the memory definitely the User?
- If the memory describes a **Third Party** (e.g., Candidate, Fictional Character), **NEVER** attribute these traits to the User.
3. **Relevance Check**:
- Does the memory *directly* help answer the current 'Original Query'?
- If it is merely a keyword match with different context, **IGNORE IT**.
4. **Freshness Check**:
- Does the memory conflict with the user's current intent? The current 'Original Query' is always the supreme Source of Truth.
# Instructions
1. **Filter**: Apply the "Four-Step Verdict" to all '<facts>' to filter out noise and unreliable AI views.
2. **Synthesize**: Use only validated memories for context.
3. **Style**: Strictly adhere to '<preferences>'.
4. **Output**: Answer directly. **NEVER** mention "retrieved memories," "database," or "AI views" in your response.
#Original Query
I want to travel during the National Day holiday. Please recommend a city I haven’t been to and a hotel brand I haven’t stayed at.
3. Next Steps
Now that you can run MemOS, you can explore more cloud platform features:
- Core Memory Operations: Learn fully how to add, retrieve, and delete memories;
- Feature Introduction: Explore more cloud platform features, such as memory filtering, multi-modal messages, knowledge bases, etc.;
- API Documentation: View complete API documentation and call examples.
4. More Resources
Understand MemOS Memory Production Process
Detailed introduction to how a message entering the system is processed into memory and effectively used in future conversations, helping you better understand the mechanism and advantages of MemOS memory.
Deep Understanding
MemOS's memory mechanism can be understood as a complete "workflow": You submit original messages → Memory is processed and produced → Scheduling mechanism arranges calls and storage based on tasks and context, and dynamically adjusts memory forms → Relevant memories are recalled when needed → Lifecycle management maintains evolution and updates simultaneously.
MemOS's memory mechanism can be understood as a complete "workflow": You submit original messages → Memory is processed and produced → Scheduling mechanism arranges calls and storage based on tasks and context, and dynamically adjusts memory forms → Relevant memories are recalled when needed → Lifecycle management maintains evolution and updates simultaneously.
MemOS in Action
MemOS provides rich project examples. Depending on your specific project, you can refer to the following materials:
- Let Financial Assistant Understand Preferences Behind Customer Behavior
- In smart investment advisory scenarios, user clicks, browsing, favorites, and communication are all behavioral trajectories that build a profile.
- MemOS can abstract these behaviors into memories, such as "Risk Preference = Conservative".
- And directly play a role when the user asks "What investment suits me?", making investment advice more professional and realistic.
- Building a Home Assistant with Memory
- A home assistant not only answers immediate questions but also remembers your todos, preferences, and family information.
- For example, "Take the kids to the zoo on Saturday" or "List points first when reminding", MemOS converts these into memories.
- Automatically plays a role in subsequent conversations, making the assistant closer to real life.
- Writing Assistant with Memory works better
- A writing assistant should not only generate content but also maintain a consistent tone and style.
- Through MemOS, user writing preferences, commonly used information, and context instructions can be remembered.
- No need to emphasize repeatedly when writing summaries or emails next time, achieving a coherent and personalized creation experience.
- MindDock Browser Extension
- MemOS-MindDock creates a unified cross-platform AI memory layer for users.
- It automatically records, organizes, and injects personal information and preferences, allowing all AIs to continuously and stably "know you".
- Coze × MemOS Plugin Tool
- Use the MemOS plugin tool listed on the Coze platform to directly access cloud service interfaces in the workflow, quickly adding long-term memory capabilities to your Agent.
- Claude MCP
- MemOS provides a way to interact with the cloud platform through MCP, directly accessing cloud service interfaces in the Claude client.