Continuous Dialogue
MemOS provides a chat interface with built-in comprehensive memory management capabilities, eliminating the need for you to manually assemble context.
1. When to Use the Chat Interface
The Chat interface provided by MemOS supports end-to-end conversation message input and output, enabling you to achieve:
- Integrated Conversational AI: Complete a conversation by calling a single interface with the user's current message, without building complex pipelines.
- Automatic Memory Processing: MemOS automatically extracts, updates, and retrieves memories, requiring no manual maintenance and ensuring no important details are missed.
- Persistent "Context": Maintain coherent understanding across turns, days, and even sessions, allowing the model to continuously "remember" the user.
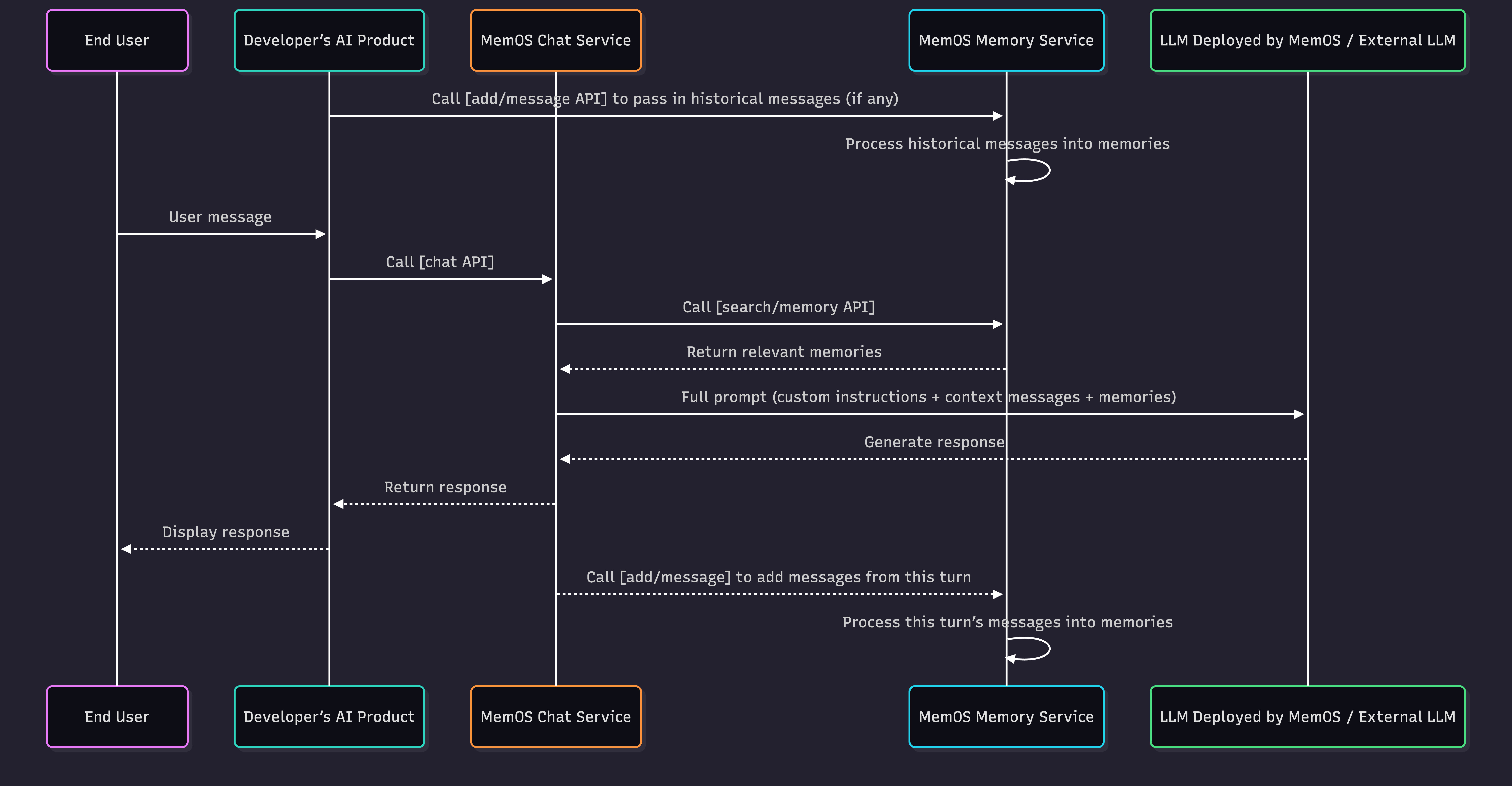
2. How It Works
The figure above illustrates the complete interaction process between the end user, your AI application, and MemOS:
- If there are historical user messages, you can first call the
add/messageinterface to write them into MemOS. - When the end user sends a message, your AI application calls the Chat interface, passing in the user message and relevant parameters.
- Upon receiving the request, MemOS sequentially completes the following processing:
- Recalls historical memories related to the current user message;
- Assembles custom instructions, current session context, and recalled user memories into a complete Prompt;
- Calls the large model to generate a response and returns the result to your AI application.
- After receiving the response, your AI application displays the content to the end user.
- Simultaneously, MemOS processes the user message and model response in the background (asynchronously by default), processing and writing them into memory.
3. Quick Start
Add Historical Messages
import os
import requests
import json
# Replace with your MemOS API Key
os.environ["MEMOS_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_API_KEY"
os.environ["MEMOS_BASE_URL"] = "https://memos.memtensor.cn/api/openmem/v1"
data = {
"user_id": "memos_user_123",
"conversation_id": "0610",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "I've booked a trip to Guangzhou for the summer vacation. What chain hotels are available for accommodation?"},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "You can consider [7 Days Inn, Ji Hotel, Hilton], etc."},
{"role": "user", "content": "I'll choose 7 Days Inn"},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "Okay, let me know if you have any other questions."}
]
}
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": f"Token {os.environ['MEMOS_API_KEY']}"
}
url = f"{os.environ['MEMOS_BASE_URL']}/add/message"
res = requests.post(url=url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(data))
print(f"result: {res.json()}")
Chat
import os
import requests
import json
# Replace with your MemOS API Key
os.environ["MEMOS_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_API_KEY"
os.environ["MEMOS_BASE_URL"] = "https://memos.memtensor.cn/api/openmem/v1"
data = {
"user_id": "memos_user_123",
"query": "I want to go out for the National Day holiday. Recommend a city I haven't been to and a hotel brand I haven't stayed at.",
"conversation_id": "0928"
}
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": f"Token {os.environ['MEMOS_API_KEY']}"
}
url = f"{os.environ['MEMOS_BASE_URL']}/chat"
res = requests.post(url=url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(data))
print(f"result: {res.json()}")
4. Usage Limits
Interface Input Limit: 8,000 tokens.
Interface Output Limit: Retrieved memory count — 25 factual memories; 25 preference memories.
5. More Features
In addition to one-click copying of the quick start code above, this interface also provides a wealth of other configurable parameters. You can refer to the explanations of the following fields to call the Chat interface for conversation during use.
For a complete list of API fields, formats, etc., please see the Chat Interface Documentation.
Filter Recalled Memories
| Feature | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Memory Filter | filter | Supports custom structured query conditions to precisely filter memories, see Memory Filter. |
| Recall Preference Memories | include_preferencepreference_limit_number | Preference memory is user preference information generated by MemOS based on analysis of user historical messages. When enabled, user preference memories can be recalled in retrieval results, "understanding the user better". |
| Retrieve Specific Knowledge Base | knowledgebase_ids | Specify the scope of project-associated knowledge bases available for this retrieval, see Knowledge Base. |
Adjust Model Response
| Feature | Field | Description & Optional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Select Model | model_name | Currently MemOS provides three models you can specify for responses. You can view detailed model introductions in Console - Model List. Optional model names: * qwen2.5-72b-instruct (Default) * qwen3-32b * deepseek-r1 |
| Custom System Prompt | system_prompt | Supports developers to customize system prompts. Defaults to MemOS built-in instructions. |
| Stream/Non-stream Response | stream | MemOS provides both streaming and non-streaming response modes. You can choose either mode based on your needs. Pass stream=true or false when calling the interface. The default output mode is: non-streaming output. |
| Key Parameters | temperature | Controls the randomness of model generated content. Lower values make the answer more stable and closer to a fixed answer; higher values make the answer more divergent and diverse. Optional value range: 0-2, default temperature value: 0.7 |
| top_p | Controls the range of candidate words available when the model generates content. Smaller values mean a narrower optional range and more convergent output; larger values mean a wider optional range and more diverse output. Optional value range: 0-1, default value: 0.95 | |
| max_tokens | Limits the maximum length of content generated by the model. Larger values allow longer generated content; generation stops when the limit is reached. Default value: 8192 |
If you want the model to better reference memory when answering, you can refer to the current MemOS default instructions when building
system_prompt. As shown below, where <memories> is the memory placeholder, which you can retain.# Role
You are an intelligent assistant with long-term memory capabilities (MemOS Assistant). Your goal is to combine retrieved memory fragments to provide the user with highly personalized, accurate, and logically rigorous answers.
# System Context
- Current time: 2025-12-16 15:51 (Please use this as the baseline for judging memory timeliness)
# Memory Data
Here is relevant information retrieved by MemOS, divided into "Facts" and "Preferences".
- **Facts**: May include user attributes, historical conversation records, or third-party information.
- **Special Note**: Content marked with `[assistant view]`, `[model summary]` represents **past inferences by AI**, and is **NOT** the user's original words.
- **Preferences**: User's explicit/implicit requirements for answer style, format, or logic.
<memories>
{memories}
</memories>
# Critical Protocol: Memory Safety
Retrieved memories may contain **AI's own speculations**, **irrelevant noise**, or **subject errors**. You must strictly execute the following **"Four-Step Verdict"**, and if any step fails, **discard** that memory:
1. **Source Verification**:
- **Core**: Distinguish between "user original words" and "AI speculation".
- If a memory carries tags like `[assistant view]`, this only represents the AI's past **hypothesis** and **must not** be treated as absolute fact from the user.
- *Counter-example*: Memory shows `[assistant view] User loves mangoes`. If the user didn't mention it, do not proactively assume the user likes mangoes to prevent circular hallucinations.
- **Principle: AI summaries are for reference only, with significantly lower weight than the user's direct statements.**
2. **Attribution Check**:
- Is the subject of the behavior in the memory "the user themselves"?
- If the memory describes a **third party** (such as "candidate", "interviewee", "fictional character", "case data"), **strictly forbid** attributing its attributes to the user.
3. **Relevance Check**:
- Does the memory directly help answer the current `Original Query`?
- If the memory is just a keyword match (e.g., both mention "code") but the context is completely different, **must ignore**.
4. **Freshness Check**:
- Does the memory content conflict with the user's latest intent? Take the current `Original Query` as the highest factual standard.
# Instructions
1. **Review**: First read `<facts>`, execute the "Four-Step Verdict", and eliminate noise and unreliable AI views.
2. **Execute**:
- Only use filtered memories to supplement background.
- Strictly abide by style requirements in `<preferences>`.
3. **Output**: Answer the question directly, **strictly forbid** mentioning system internal terms like "memory bank", "retrieval", or "AI view".
One-click Add Message, Process as Memory
| Feature | Field | Description & Optional Values |
|---|---|---|
| Enable this feature | add_message_on_answer | When this feature is enabled, MemOS automatically stores user messages and model responses and processes them into memory. Developers do not need to manage this separately. Pass add_message_on_answer=true or false when calling the interface. Currently enabled by default. |
| Associate More Entities | agent_idapp_id | Unique identifier for associating current user conversation messages with entities like Agents, apps, etc., facilitating subsequent memory retrieval by entity dimension. |
| Async Mode | async_mode | Controls the processing method after adding messages, supporting both asynchronous and synchronous modes, see Async Mode. |
| Custom Tags | tags | Add custom tags to current user conversation messages for subsequent memory retrieval and filtering, see Custom Tags. |
| Meta Info | info | Custom meta information fields used to supplement current user conversation messages and used as filtering conditions in subsequent memory retrieval. |
| Write to Public Memory | allow_public | Controls whether memories generated from current user conversation messages are written to project-level public memory for sharing among all users under the project. |
| Write to Knowledge Base Memory | allow_knowledgebase_ids | Controls whether memories generated from current user conversation messages are written to specified project-associated knowledge bases. |
6. Comparison of Memory Operation Interfaces
| Comparison Dimension | Chat Interface | Memory Management Interface |
|---|---|---|
| Multimodal Memory | Currently not supported for input | ✅Supported for input and retrieval |
| Tool Memory | Currently not supported for input/retrieval | ✅Supported for input and retrieval |
| Memory Management | ✅Automatic user memory management | Manually add messages, retrieve memories |
| Context Engineering | ✅Automatic assembly | Manual assembly |
| Model Response | ✅Free use of specified model list Basic model parameters | Call external models yourself ✅Rich model parameters |
| Complexity | ✅Simple, out of the box | Medium, requires development |
| Typical Use Cases | General AI conversation applications Business PoC / Rapid validation | Complex Agent applications Deep integration with business systems |